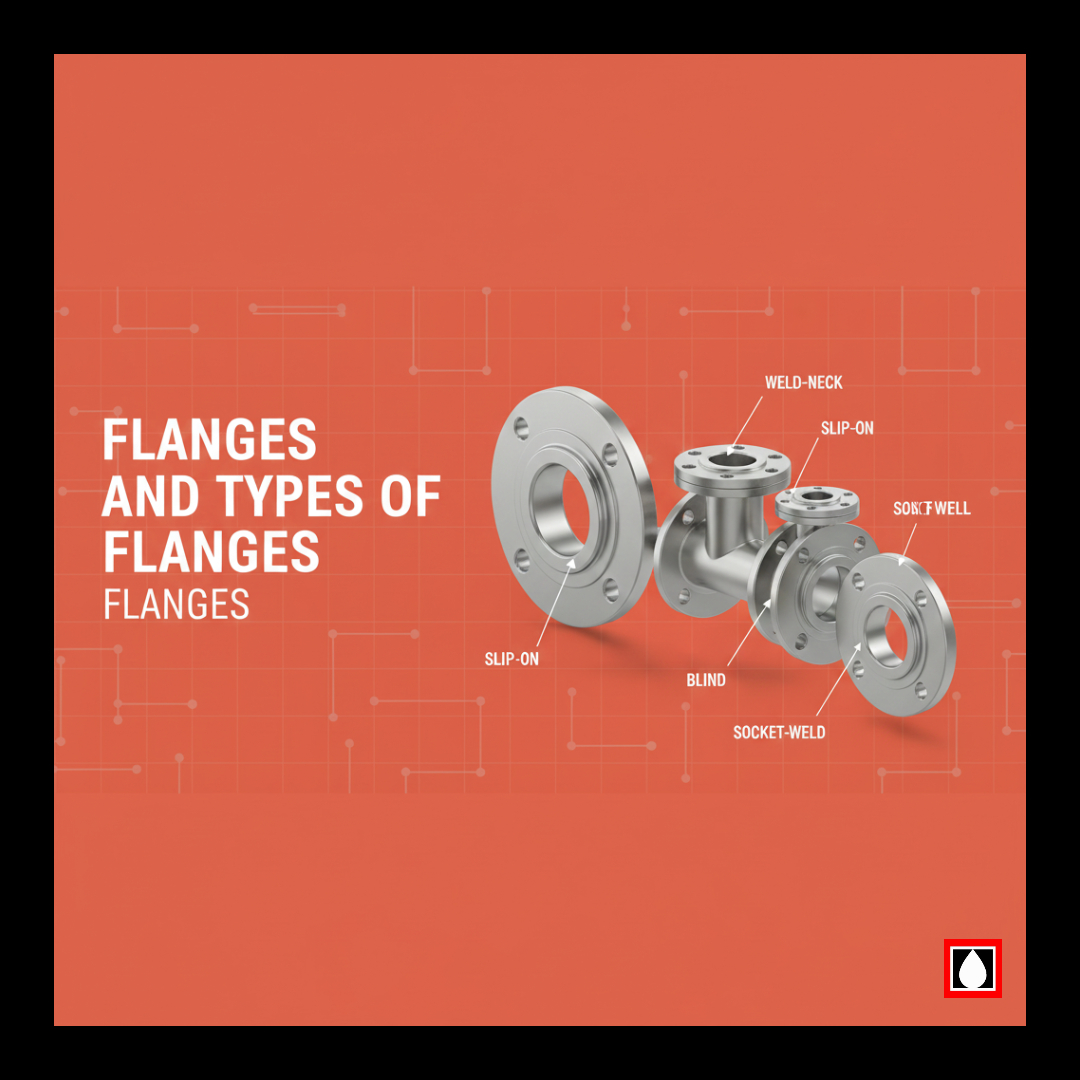
Types of flanges and their applications
A flange is readily defined as a connecting piece that is utilized on pipes, valves, pumps, and other relevant equipment in pipelines. It can be categorized into different types depending on the specific type of use, environment, and working conditions it is to be used at. Here are some common types of flanges and their typical applications:Here are some common types of flanges and their typical applications:
- Applications: Weld neck flanges are used in different and challenging environment including petrochemical industry, oil and gas industry and power stations. They afford more reinforcement and support to the pipe and due to this they are applicable in critical services.
Slip-On Flange (SORF):
- Applications: They are favourable for low pressure applications and can also be applied in critical applications since the bolted joint is not subjected to pressure. These are easy in installation and may be used in system where their disassembly may not be frequent.
Socket Weld Flange (SWRF):
- Applications: Socket weld flanges are applied where small diameter high pressure pipe is to be utilized. They exhibit good fluidity and are ideal for use where high pressure/temperature is involved.
Threaded Flange (THRF):
- Applications: Threaded flanges are normally incorporated in low pressure and small bore piping services. They are helpful for systems in which continual connection and disconnecting is required.
Blind Flange (BLRF):
- Applications: The blind flanges serve purposes of sealing of the end of a pipe or a vessel opening. They are used for instances where the system needs frequent checking or repairing as they help in indicating when it is time to do so.
Lap Joint Flange (LJRF):
- Applications: Lap joint flanges are applied in systems that need simple blind positioning of flange faces. Many are utilized in low-stress and unsophisticated applications.
Orifice Flange:
- Applications: Orifice flanges are used in flow measurement applications. They have a small orifice hole that allows for precise flow rate measurement using orifice plates.
Swivel Ring Flange:
- Applications: Swivel ring flanges are used in subsea and offshore applications. They allow for rotational movement and flexibility in piping systems.
Expander Flange:
- Applications: Expander flanges are used to increase the pipe size gradually in high-pressure systems. They reduce turbulence and pressure drop.
Reducer Flange:
- Applications: Reducer flanges are those types of flanges which is mainly used to connect pipes of different diameter in a piping components. They are used in connecting one pipe diameter to another with ease.
Ring-Type Joint Flange (RTJ):
- Applications: RTJ flanges are used in high-pressure and high-temperature applications, such as in the oil and gas industry. They provide excellent sealing under extreme conditions.
Square Flange:
- Applications: Square flanges are specified for where square connect is needed for instance in HV AC and some architectural purposes.
Groove Flange:
- Applications: Groove flanges come in handy in systems where the flange has to be keyed into the pipe, for a better hold. They are mostly applied in fire protection mechanisms.
Tongue and Groove Flange:
- Applications: Tongue and groove flanges are employed where the concentricity and gasketing are very important like in high pressure and high temperature uses.
Custom Flanges:
- Applications: Thus, it is possible to manufacture flanges that meet certain characteristics and requirements which cannot be addressed by normal flanges. These are in most cases applied in certain segments of the industries and certain kinds of piping systems.
types of flanges in piping, temperature and the compatibility of the two surfaces in contact together with the demands of the application in question. Skillful selection results in the right design of the grade, material, and type of the piping system that meets the needs of safety, reliability, and functionality.
Special flanges
Except the most used standard flanges, there are still a number of special flanges such as:
- Orifice flanges
- Long welding neck flanges
- Weldoflange/Nipoflange
- Expander flange
- Reducing flange
- Special flanges
How many types of flanges are there
There are many different types of flanges, but some of the most common include:There are many different types of flanges, but some of the most common include:
- Welding neck flanges: These flanges are of long neck having the neck welded to the pipe. It is mainly applied for high pressure services.
Welding neck flanges
- Socket weld flanges: The flanges that are used have a socket welded to it and the pipe is connected to the other end. These are common in settings that are not highly competitive usually in areas that do not require a lot of competition.
Socket weld flanges
- Threaded flanges: These flanges have bored holes which have threading where they can be fitted to the pipe. These are generally employed in low pressure services.
Threaded flanges
- Blind flanges: These flanges have a solid face and they are applied on an opening of the pipe which is often blocked.
Blind flanges
- Reduced bore flanges: These flanges are less in diameter compared to the pipe they join in or with the attachment of which they are in use. They are ordinarily employed to lessen the rate of fluid passing through the pipe.
Reduced bore flanges
- Raised face flanges: These flanges have raised face which is used in giving a better sealing surface to the flanges.
Raised face flanges
- Ring joint flanges: The two following flanges have a feature of a ring joint which helps in improving the sealing of the flanges.
Ring joint flanges
- Lug flanges: These flanges have lugs that are used to connect them to the pipe. They are typically used for low-pressure applications.
Lug flanges
The type of flange that is used depends on the application and the pressure rating of the pipe.
Here are some of the factors to consider when choosing a flange:
- The type of flange that is going to be used in a particular system depends on the use of the pipe and its pressure category.
- Here are some of the factors to consider when choosing a flange:Here are some of the factors to consider when choosing a flange:
- Pressure rating: This writing must bear the pressure of the flange due to the flowing of the fluids through flange.
- Temperature rating: Its thickness must also suffice when it comes to temperature of the fluid that will be passing through the flange.
- Material: This flange must therefore be of a material that is correct in the type of fluid going to flow within it.
- Size: Flange has to be of the correct size of the pipe with which it will be connected.
- Cost: The flange must be affordable.
Complete Oil and Gas Industry Practical Training Course
Complete Oil and Gas Industry Practical Training Course is a self-learning, practical program powered by industry expertise. Log in to explore, practice real scenarios, and grow industry-ready skills.
- pipenet
- pipesim
- HTRI
- olga
How flanges are made
A flange is a critical component of the piping systems that offer provision for assembly, disassembly and easy replacement or any other activity to be accomplished on the system. Cooperage flanges can be manufactured through various methods, which are forging, casting, and cutting from rolled plate materials
Flanging is one of the widely used processes in the production of flanges and this involves forging. Forged flanges are produced by placing a ferrous or non-ferrous material through a process of heating and applying pressure on that material to make it to fit in a specific mold known as die. Forging manufacturing process yields a more durable material than when you cast or cut from a plate which is crucial in high-pressure and high temperatures.
Casting is one of the processes of manufacturing in which molten metal is poured into a mold followed by a process of cooling and solidification in the form of a flange. The casting process can be used under moderate to low pressure and is mostly carried out for non-critical applications. It is not as strong as forged ones, but the cast flanges are comparatively inexpensive and can save a lot of time, which is perfect for non-critical work and less intense settings.
Flanges can be fashioned from rolled plate materials by first punching the plate with a large press and then shaving it into form. Smashing flanges is essentially cheaper and can be utilized in manufacture of large diameter flanges
Also, once in production of the flange, there are close tolerances perhaps involving further machining to ensure it meets the tolerance of the intended use and that the face of the flange is clean and compatible with the gasket to prevent leakages.
In conclusion, there are three methods of manufacturing flanges which are forging, casting and cutting the rolled plate materials with an option of further machining. The manufacturing process chosen depends with the application needed, cost, type of material and the other factors.
What are flanges
Flanges are gaskets used on the pipelines to join pipes and other accessories like valves, pump etc. They serve a specific purpose of making sure that the system is free from flaws and is fully operational. Before explanation of the term, it is crucial to state that flanges are usually flat or even raised rings with bolt holes through which they can be tightened and secured to other flanges or equipment. Here are some key aspects of flanges:Here are some key aspects of flanges:
Connection: While being one of the most vital forming methods for pipes and pipe components like valves, fittings and equipment, flanges offer a method of joining two or more pipes or pipe components in a given piping system. They design a connection that can be put together or taken apart should the need arise.Teachers as agents of innovation: An investigation into the use of knowledge-building in the context of teachers’ professional development and practiceParamount among the findings of this work was the determination of the type of joint that the students made.
Sealing: Between two confronting flange faces, there may be gasket or the sealing material inserted. These gaskets assist in the formation of a leak-proof barrier thus making flanges vital tools in piped systems.
Strength: Dependent on their application, flanges are intended for pressure, temperature and mechanical load-class ranges. It supports connected components & also helps to carry out stresses evenly through the joint area.
Versatility: Flanges can be categorized according to their type, size, and function depending on the needs and the environment that it will be used into. This mainly has to do with system pressure and temperature as well as other essential characteristics of the application.
Bolted Connection: Connecting committees are generally implemented with flanges and bolts or studs are fixed in between flanges . For this, the number and size of bolts vary with the size of the flange and the pressure allowance of the system. Bolt tension is a critical factor which has to be ensured for the appropriate performance of the joined parts.
Types: Some of the most common examples of flanges are weld neck flanges, slip-on flanges, socket weld flanges, threaded flanges, blind flanges, lap joint flanges, orifice and many others. Semi flexible types are meant to be used for specific purposes and thus have different properties as compared to fully flexible types.
Materials: Currently, flanges can be manufactured in carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel and non-metals among others. This is the type of material chosen based on the fluid to be transported, degree of corrosion resistance and other things.
Standards: Therefore, flanges are made to meet standard requirements or codes that include the flare and the API Standard for Wellsite Fabricated Flanges and Connections, The ASME B31.3 Process, and others. These standards describe the size, material, and the requirement of flanges.
Again, flanges are critical working items in most piping and equipment needs across factions such as the oil and gas faction, factions in the production of petrochemicals and chemicals, factions in power generation, among others. Flanges have to be chosen well and used in accordance to all the requirements of their installation and further maintenance in order to guarantee safe, reliable, and efficient functioning of all systems where they are used.
Flanges are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Piping systems: Flanges are widely employed for coupling pipes in several spheres, these may be oil and gas, chemical, and water treatment industries.
Flanges in piping system
- Machinery: These are parts used to join various parts and components in operation such as in pumps and other valves.
Flanges in machinery
- Structural applications: Connecting devices such as Fasteners and gaskets are employed whereby flanges are used in joining beams and column.
Flanges in structural applications
- Transportation: Flanges are used to connect components in vehicles, such as cars and trucks.
Flanges in transportation
Another common element that comes in various forms and is used with many applications in various industries is a flange. Some of the most common types of flanges include:Some of the most common types of flanges include:
- Welding neck flanges: These flanges are either termed as long-neck flanges, which is a pipe that is welded to the neck part. It is normally employed in high pressure applications and typical applications include manufacturing of fuel injection pumps and so on.
- Socket weld flanges: These flanges have a socket that is welded to the pipe, The shape of the flange allows a gasket to be placed between the flange and the pipe. They are generally applied in lower stress or power transmission systems.
- Threaded flanges: These flanges also have bolt holes and the bolts used passes through it in order to connect the flange to the pipe. It is also common with low pressure applications.Their advantage is that they are relatively cheap.
- Blind flanges: These flanges are faced and are designed to seal off an opening on a pipe.
- Reduced bore flanges: These flanges have a Bore less than the Pipe connected to them refer to NPS and Nominal Bore. They are mostly applied to decrease the rate of the flow of fluid within the pipe.
- Raised face flanges: These flanges also include raised face which is intended to be employed in the creation of bigger seal between the flanges.
- Ring joint flanges: These flanges also contain ring joint which is useful to help in creating a better seal of the flanges.
- Lug flanges: These flanges contain lugs that are used to attached the flange to the pipe in question. They are normally applied in low pressure services.
There are two categories of flange and the kind to be used depends on the application and the pipe pressure rating. One should seek the services of a suitable engineer while selecting a flange. The engineer can assist you on better decision on which flange to use for your specific application.
It thus becomes clear that flanges can be used in as a big part of different types of systems. These are used to join pipes and other components and are employed in a vast range of industries for they are secure and dependable.
Flanges and Fittings
Flanges and fittings are essential components of piping systems. They are used to connect pipes, valves, and other components together. Flanges are typically made of metal, but they can also be made of plastic or other materials. Fittings are also made of metal, plastic, or other materials.
There are many different types of flanges and fittings, each with its own specific design and purpose. Some of the most common types of flanges include:
- Welding neck flanges: These flanges have a long neck that is welded to the pipe. They are typically used for high-pressure applications.
- Socket weld flanges: These flanges have a socket that is welded to the pipe. They are typically used for lower-pressure applications.
- Threaded flanges: These flanges have threaded holes that are used to connect them to the pipe. They are typically used for low-pressure applications.
- Blind flanges: These flanges have a solid face and are used to block off a pipe opening.
- Reduced bore flanges: These flanges have a smaller bore than the pipe they are connected to. They are typically used to reduce the flow of fluid through the pipe.
- Raised face flanges: These flanges have a raised face that is used to provide a better seal between the flanges.
- Ring joint flanges: These flanges have a ring joint that is used to provide a better seal between the flanges.
- Lug flanges: These flanges have lugs that are used to connect them to the pipe. They are typically used for low-pressure applications.
Fittings are used to connect pipes and other components in a variety of ways. Some of the most common types of fittings include:
- Elbows: Elbows are used to change the direction of a pipe.
- Tees: Tees are used to branch off a pipe.
- Reducers: Reducers are used to reduce the diameter of a pipe.
- Unions: Unions are used to disconnect pipes without having to cut them.
- Caps: Caps are used to seal the end of a pipe.
- Plugs: Plugs are used to block off a hole in a pipe.
The type of flange or fitting that is used depends on the application and the pressure rating of the pipe. It is important to consult with a qualified engineer when choosing a flange or fitting. The engineer will be able to help you choose the right flange or fitting for your application.
Flanges and fittings are an essential part of piping systems. They provide a secure and reliable way to connect pipes and other components, and they are used in a wide variety of industries.
When working with flanges and fittings, it is important to be aware of the safety risks involved. Some of the potential hazards include.
- Electrical shock: Flanges and fittings can come into contact with electrical wires, which can cause electrical shock.
- Fire: Flanges and fittings can become hot, which can cause a fire.
- Explosion: Flanges and fittings can rupture, which can cause an explosion.
- Chemical exposure: Flanges and fittings can come into contact with hazardous chemicals, which can cause chemical exposure.
To avoid these hazards, it is important to take the following safety precautions:
- Wear safety glasses and gloves when working with flanges and fittings.
- Make sure that the flanges and fittings are properly grounded to prevent electrical shock.
- Do not work with flanges and fittings that are hot or damaged.
- Be aware of the hazardous chemicals that may be present in the area.
By following these safety precautions, you can help to prevent accidents and injuries when working with flanges and fittings.