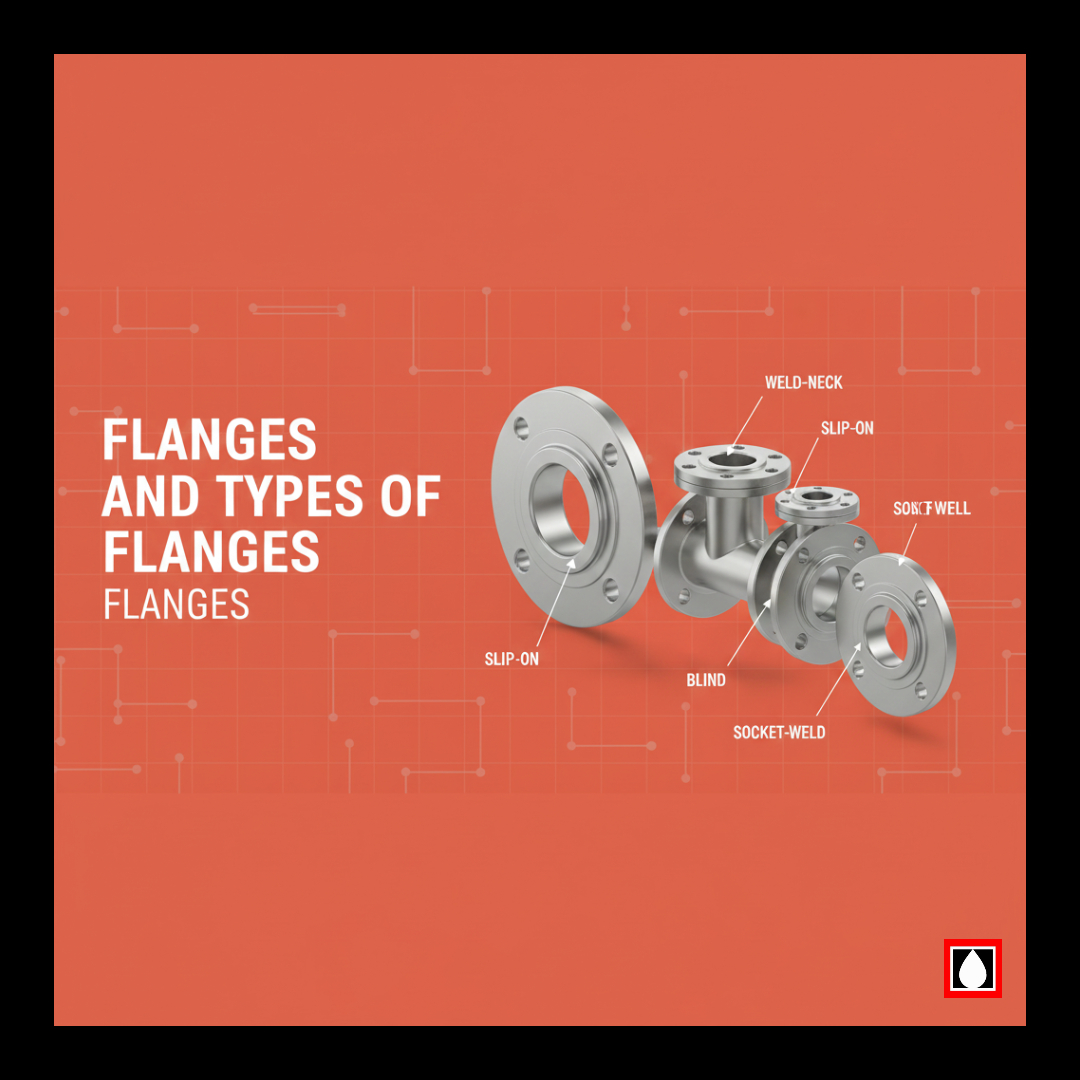
About the CAESAR II Documentation
Caesar piping stress analysis is defined as the application of the Caesar II software in predicting the stress and deformation pattern of piping systems. PIPING ENGINEERS AND FACULTY NAME Piping Planet’s Caesar II is one of the most popular piping engineering software that is employed to analyze the strength and behavior of system piping. The main objectives of piping stress analysis using Caesar II are: 1. Stress calculation: It for performing stress analysis to obtain the stresses and deformation of a piping system under various loads like pressure, thermal expansion, weight & other loads. 2. Compliance with codes and standards: Using Caesar II, engineers are able to verify that all the design of the piping system complies with the design specifications put down by various codes and standard like ASME B31. 1 and ASME B31. 3. It carries out computation and verifications using these codes in order to accomplish the structural and compliance of the system. 3. Evaluating and mitigating stress-related issues: Thus, through stress and deformation, the engineers will be able to tell some of the ‘hot spots’ in a piping system, that is, parts with high stress, regions with high displacement or the support loads exerted. They can then make design modifications and recommend other accommodations to lessen the impacts as detailed below. 4. Assessing system reliability: Piping stress analysis enables one to establish the conditions under which piping system is safe to work. Thus, stresses help engineering to show that all the related loads are sustained by the piping components and that the chances of failure from fatigue or creep are lowered. The analysis of piping stress in Caesar involves certain key processes they include modeling of the system, operational conditions that are set, loads that are applied, system analysis, and review of the results. The results can be obtained in form of output reports with stress values, support loads, displacement and other related data. In conclusion, caesar piping stress analysis is essential in assessing the structural strength as well as the conformity of the piping systems and their operation to a particular society code.